Compare PP and PE packaging
29/03/2025Compare PP and PE Packaging: PP (Polypropylene) and PE (Polyethylene) are both thermoplastics known for being water-resistant, food-safe, and recyclable. However, PP packaging is harder, more durable, and heat-resistant (-20°C to 120°C) with a glossy surface, making it ideal for woven bags, plastic containers, and microwave-safe products. On the other hand, PE packaging is softer, more flexible, and has lower heat resistance (-50°C to 80°C), offering high transparency, which makes it suitable for plastic bags, food wrap, and shrink film. Although PP recycling is more challenging than PE recycling, PP offers superior mechanical impact resistance, enhancing its durability for heavy-duty packaging.
To fully understand these two types of packaging, we need to explore their distinct characteristics, applications, and environmental impact in detail.
Introduction to PP and PE Packaging
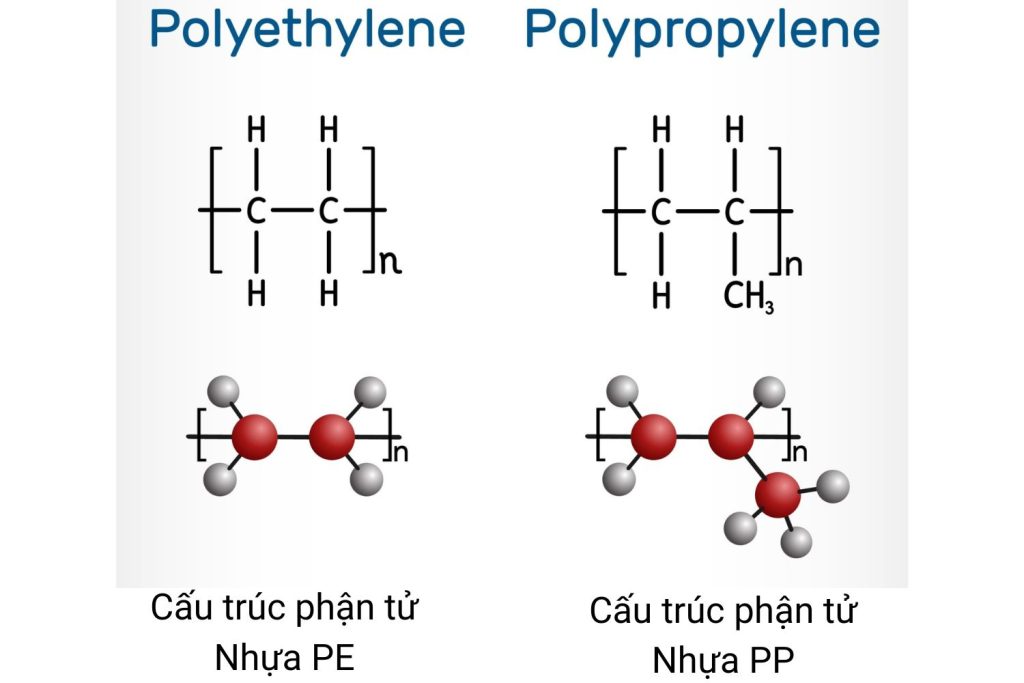
When discussing packaging, two primary types of plastic that cannot be overlooked are PP and PE. Both are polymers, yet their distinct structures and properties result in diverse applications in everyday life.
Polypropylene (PP) Plastic
Polypropylene (PP) is a semi-crystalline polymer known for its superior hardness and durability compared to many other materials. Thanks to its excellent heat resistance, PP is widely used in the production of rigid food packaging such as yogurt containers and butter tubs. In addition, PP is extensively applied in other industries, including reusable medical equipment, automotive parts, household plastics, and construction materials.
Polyethylene (PE) Plastic
In contrast, polyethylene (PE) is an amorphous polymer that is generally softer and easier to process compared to PP. Due to these properties, PE is an ideal choice for soft food packaging, bags, wraps, bottles, and toys. Its design flexibility and low cost have made PE one of the most popular plastics in the packaging market.
Properties of PP Packaging
PP (polypropylene) and PE (polyethylene) are two common types of plastic widely used in our daily lives. Although they share some similarities, each has distinct characteristics that result in different applications and features. This article will provide a detailed overview of the properties, advantages, and differences between these two plastics, helping you better understand these widely used materials.
Polypropylene (PP) is a type of plastic known for its excellent heat and chemical resistance, lightweight nature, and ease of processing. These qualities have made PP one of the most widely used plastics across various industries, from packaging and construction to the automotive sector.
High Heat and Chemical Resistance
One of PP’s outstanding advantages is its excellent heat resistance and chemical durability. PP melts at approximately 160-170°C, significantly higher than PE (polyethylene). This property allows PP products to withstand higher temperatures during use, transport, or processing.
PP also boasts strong chemical resistance, effectively withstanding acids, alkalis, solvents, and other oxidizing agents. As a result, PP is ideal for manufacturing packaging products and containers designed to hold strong chemicals, such as bottles and industrial chemical storage tanks.
Lightweight and Easy to Process
With a density of only about 0.9 g/cm³, PP is considered one of the lightest plastics. This lightweight characteristic makes PP products easier to handle and transport, especially in industries such as automotive manufacturing and logistics.

Additionally, PP is also highly versatile and can be processed using various methods such as molding, blow molding, and injection molding. This flexibility is a significant advantage, allowing PP to be used in the production of a wide range of products, from simple containers and bottles to complex automotive parts.
Easy to Recycle and Environmentally Friendly
Another key advantage of PP is its excellent recyclability. PP can be recycled multiple times without losing its mechanical properties. This not only helps reduce plastic waste but also contributes to environmental protection.
Moreover, PP is considered a relatively eco-friendly plastic. Its production process consumes less energy and releases fewer harmful emissions compared to some other plastics.
Key Applications of Polypropylene (PP)
Thanks to its outstanding characteristics such as high heat and chemical resistance, lightweight nature, and strong recyclability, PP has been widely adopted across various industries:
- Packaging and Wrapping: PP is extensively used in the production of packaging products such as containers, bottles, bags, and food wraps. These products not only protect the contents effectively but are also easy to recycle.
- Automotive and Transportation: In the automotive industry, PP is used to manufacture various components such as dashboards, bumpers, and headlights. Due to its lightweight and durable properties, PP helps reduce vehicle weight and improve fuel efficiency.
- Electronics and Household Products: PP is widely applied in making electronic and household products such as washing machine casings, refrigerator parts, and remote control covers.
- Construction: In the construction sector, PP is utilized for manufacturing water pipes, gas pipes, and pipe fittings. These products are known for their durability and heat resistance.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: Thanks to its safety and easy-to-clean properties, PP is ideal for producing medical equipment and pharmaceutical packaging.
In conclusion, with its outstanding advantages, polypropylene (PP) has become one of the most commonly used plastics today, meeting demands across packaging, industry, and various other sectors.
 |  |  |
Characteristics of Polyethylene (PE)
Polyethylene (PE) is another widely used plastic material, commonly applied across various industries, from packaging to household products. PE possesses distinct characteristics that set it apart from PP, resulting in different applications and performance features.

High Durability and Flexibility
One of the outstanding advantages of PE is its high durability and flexibility. PE exhibits excellent resistance to impact, tearing, and breakage, while also being highly flexible. Products made from PE are less prone to breaking or damage.
Thanks to these properties, PE is highly suitable for manufacturing durable products such as bags, packaging, bottles, etc. These products can withstand impact and drops without being damaged.
Low Heat Resistance
However, one limitation of PE compared to PP is its lower heat resistance. PE’s melting point is only about 110-130°C, significantly lower than that of PP. Consequently, PE products cannot endure high temperatures like PP products.
This limits PE’s applications in certain fields such as hot food packaging and high-temperature processing technologies.
Low Density and Easy Processing
Similar to PP, PE is a low-density plastic, with a specific gravity of only about 0.91-0.96 g/cm³. This makes PE products lighter, which is advantageous for various applications, particularly in transportation.
Moreover, PE is easy to process using various methods such as molding, blowing, and casting. This enhances its flexibility and usability in manufacturing.
Main Applications of Polyethylene (PE)
With its advantages such as durability, flexibility, lightweight properties, and ease of processing, polyethylene (PE) is widely used across many industries:
- Packaging and Wrapping: PE is one of the most commonly used plastics for producing packaging and wrapping materials such as plastic bags, food packaging, bottles, etc. These products require durability and flexibility to effectively protect the contents.
- Household Products: Many household items like containers, bottles, bags, and trash bins are made from high-density PE due to its impact resistance and durability.
- Agriculture: In the agricultural sector, PE is used to manufacture irrigation pipes, protective nets, and produce storage bags. These products require durability, flexibility, and resistance to harsh conditions.
- Construction: In construction, PE is used for water pipes, gas pipes, and pipe fittings due to its ability to withstand low temperatures and maintain strong mechanical properties.
- Medical and Pharmaceutical: Similar to PP, PE is also used in the production of medical instruments and pharmaceutical packaging due to its safety and ease of cleaning.
With its distinctive advantages in durability, flexibility, and lightweight properties, polyethylene (PE) has become a widely applied plastic in various aspects of daily life.
Comparison Between Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene (PE)
Although both PP and PE are common types of plastic, they have significant similarities and differences in terms of composition, properties, and applications.
| Criteria | Polypropylene (PP) | Polyethylene (PE) |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | C3H6 (propylene polymer) | C2H4 (ethylene polymer) |
| Mechanical Strength | Higher, more rigid than PE | Lower, softer than PP |
| Tensile Strength | 30–40 MPa | 10–20 MPa |
| Heat Resistance | Better heat resistance (up to 100–130°C) | Lower heat resistance (about 80–100°C) |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, alkalis, and solvents | Superior chemical resistance in harsh environments |
| Elasticity | Less flexible, becomes brittle at low temperatures | More flexible, does not become brittle in cold conditions |
| Processability | Easy to process, ideal for complex shapes | Easy to process but more limited than PP |
| Main Applications | Packaging, pipes, containers, automotive parts | Plastic bags, food wrap, water bottles, pipes |
| Density | 0.90–0.91 g/cm³ (lighter than PE) | 0.91–0.97 g/cm³ |
| Transparency | Easier to achieve transparency (common in clear packaging) | Typically more opaque, requires treatment for transparency |
| Cost | Generally higher than PE | Lower than PP, more widely used |
| Recyclability | Easily recyclable but less common than PE | Easily recyclable and more commonly reused |
Physical Properties
In terms of physical properties, PP and PE exhibit both similarities and differences:
- Density: PP is lighter, with a density of approximately 0.9 g/cm³, compared to PE’s range of 0.91–0.96 g/cm³.
- Melting Point: PP has a higher melting point (about 160–170°C) than PE (about 110–130°C).
- Mechanical Durability: PE is generally more durable and flexible, with better resistance to impact and tearing.
- Chemical Resistance: PP offers superior chemical resistance, particularly against acids, alkalis, and chemical solvents.
Processing Capabilities
Both PP and PE are easy to process and can be manufactured through various methods such as molding, blowing, and injection molding. However, PE’s higher flexibility allows for a broader range of applications in processing.
Applications
Due to their distinct properties, PP and PE are applied in different industries:
- Polypropylene (PP): Commonly used in the automotive industry, household items, and products requiring higher durability. Items like car parts, automotive interiors, and durable containers are often made from PP due to its excellent heat resistance and chemical stability.
- Polyethylene (PE): PE is widely preferred for packaging and wrapping products because of its flexibility and durability. Examples include plastic bags, food wrap, and water bottles, which provide effective protection while resisting impact during transportation.
Overall, while both plastics offer versatile applications, their differing physical and chemical properties create distinct markets for each material. Advancements in technology will continue to expand their potential uses, meeting a variety of consumer needs.
Pros and Cons of Polypropylene (PP) and Polyethylene (PE)
Advantages of Polypropylene (PP)
- Superior Heat Resistance: PP’s higher melting point allows its products to perform better in extreme temperatures, making it ideal for industrial and automotive uses.
- Excellent Chemical Resistance: PP products resist acids, alkalis, and solvents, ensuring longevity and reliability in critical environments such as food processing and healthcare.
Disadvantages of Polypropylene (PP)
- Lower Flexibility: PP’s rigidity limits its use in applications requiring pliability, such as flexible bags or soft packaging.
- Higher Production Cost: PP’s complex manufacturing process often leads to higher production costs, making it less competitive in price-sensitive markets.
Advantages of Polyethylene (PE)
- Outstanding Flexibility and Durability: PE’s flexibility makes it perfect for packaging and wrapping materials. Its elasticity and impact resistance help protect goods effectively.
- Easy Processing: PE’s versatility in processing methods like molding, blowing, and extrusion allows for efficient mass production, reducing costs.
Disadvantages of Polyethylene (PE)
- Lower Heat Resistance: PE’s limited heat resistance restricts its application in high-temperature environments, such as hot food packaging or industrial equipment.
- Weaker Chemical Resistance: Compared to PP, PE is less resistant to aggressive chemicals, limiting its reliability in certain applications.
How to Distinguish PE and PP Packaging
- By Touch and Feel
- PE Packaging: Soft, smooth texture. Difficult to stretch and returns to its original state when crumpled.
- PP Packaging: Harder and slightly rough. Tends to retain creases when crumpled.
 |  |
- Transparency and Color
- PE Packaging: Lower transparency, slightly hazy or opaque. Uniform color with minimal gloss.
- PP Packaging: Higher transparency, shinier surface, and more visually appealing.
- Sound When Crumpled
- PE Packaging: Produces a faint or unclear sound, giving a soft feel.
- PP Packaging: Produces a distinct “crinkling” sound, giving a sturdier feel.
- Burn Test
- PE Packaging: Burns quickly with a yellow flame and a scent similar to burning candle wax. When burned, the plastic melts into droplets without leaving ash.
- PP Packaging: Burns with a yellow flame and a stronger odor compared to PE. It often produces black smoke when burned.
Conclusion
Through this article, we have explored two of the most common types of plastic today: polypropylene (PP) and polyethylene (PE). Both materials have their own advantages and disadvantages, which influence their practical applications. The choice between PP and PE depends on various factors, including usage needs, environmental conditions, and production costs.
This highlights the importance of understanding and thoroughly researching before making production decisions. Hopefully, this article provides you with an informative overview of these two types of plastic, helping you make the best choices for your project.