What is HDPE Plastic? Key Features and Practical Applications
23/04/2025HDPE, or High-Density Polyethylene, is a thermoplastic widely used in everyday life. It is found in simple household items such as bottles and packaging, as well as in more complex applications like water pipes and construction materials. With its high durability, good heat resistance, ease of processing, and safety for human health, HDPE is considered one of the most important and commonly used plastic materials today. This article delves into a deeper understanding of HDPE, highlighting its key characteristics and exploring its wide range of applications across different industries.
Structure and Properties of HDPE
Structure of HDPE
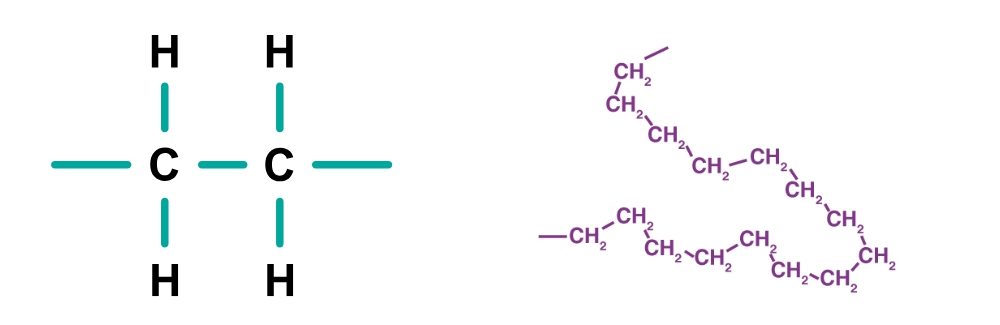
HDPE stands for High-Density Polyethylene. It is a thermoplastic made from ethylene monomers derived from petroleum. HDPE has a tightly packed molecular structure, with a higher density than conventional types of polyethylene (PE).
HDPE features a linear molecular chain, where the molecules are closely bonded together, forming a strong and durable network. This structure gives HDPE superior properties compared to other materials.
Would you like me to continue translating the rest of the article?
Summary Table of the Chemical and Physical Properties of HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene):
| Property | Description |
|---|---|
| Chemical Structure | A polymer composed of repeating ethylene (-CH2-CH2-) chains with high molecular density and fewer branches than LDPE. |
| Density | 0.93 – 0.97 g/cm³ |
| Tensile Strength | 20 – 31 MPa (depending on the type of HDPE and processing conditions). |
| Elongation at Break | 10 – 100% |
| Melting Temperature | 120 – 130°C |
| Service Temperature | -40°C to 80°C |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to acids, alkalis, organic solvents, and many other chemicals; however, it has poor resistance to strong oxidizers. |
| Permeability | Excellent resistance to water and gas permeability, especially steam. |
| Hardness | Higher than LDPE, while still retaining moderate flexibility. |
| Electrical & Thermal Conductivity | HDPE is a good electrical and thermal insulator. |
| Recyclability | Classified as recycling code #2; can be easily recycled into new products. |
| Color | Naturally translucent but can be colored easily. |
| Common Applications | Used in manufacturing plastic bottles, water pipes, plastic bags, toys, chemical containers, construction materials, and waterproof liners. |
Why Is HDPE So Popular?
Versatile Formability
Like many other thermoplastics, HDPE has excellent formability. This means that when heated to its melting point, HDPE becomes pliable and can easily be molded into various shapes using different methods such as injection molding, extrusion, blow molding, and thermoforming. Once cooled, HDPE retains its new shape, providing great flexibility in design and manufacturing.
Thanks to this ease of forming, HDPE is widely used in the production of complex-shaped items such as plastic bottles, jars, containers, children’s toys, and more. Designers are free to create aesthetically pleasing products that also meet specific functional needs.
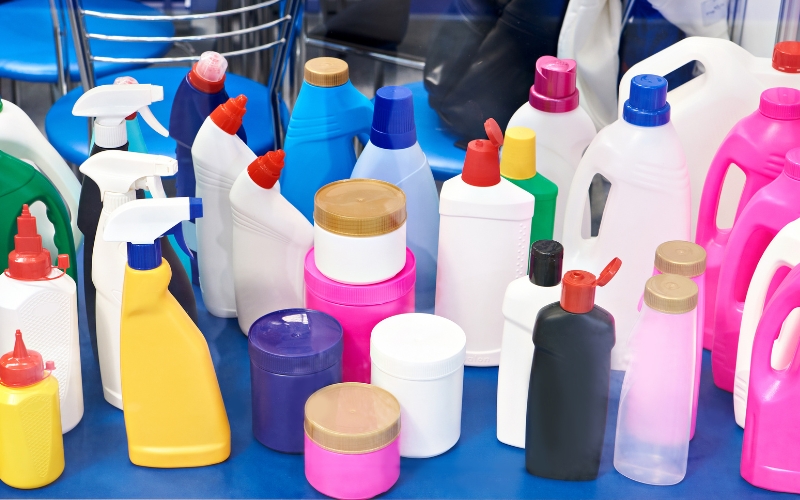

For example, in the food industry, HDPE is used to manufacture water bottles, milk jugs, food containers, and more. These products are not only visually appealing but also meet hygiene and food safety standards. The flexible formability of HDPE plays a significant role in the advancement of food packaging and preservation technologies.
High Mechanical Strength
One of HDPE’s most outstanding advantages is its high mechanical strength. It has excellent resistance to stress, impact, and abrasion. The linear molecular structure with tightly packed polymer chains gives HDPE greater hardness and strength compared to other types of polyethylene.
This property allows HDPE products to have a long service life and reduces damage during use. The real-world application of HDPE in manufacturing load-bearing products such as water pipes, chemical containers, and automotive parts clearly demonstrates its mechanical durability.
Thanks to its high strength and impact resistance, HDPE is also used in the production of construction materials such as roofing sheets and drainage pipes. Especially in construction, HDPE’s durability helps extend the lifespan of structures and reduces maintenance and repair costs.
Chemical and Corrosion Resistance
HDPE exhibits excellent resistance to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, bases, salts, and many organic solvents. This is due to its highly stable molecular structure, which is not easily broken down by external chemical reactions.
The chemical and corrosion resistance of HDPE is especially important in applications involving the storage and transportation of chemicals, wastewater, and corrosive substances.
Ví dụ, các ống dẫn nước làm từ HDPE được sử dụng rộng rãi trong các hệ thống cấp thoát nước, hệ thống tưới tiêu, và cả trong các ngành công nghiệp hóa chất. Nhờ khả năng chống ăn mòn, các ống HDPE có thể vận chuyển nước sạch, nước thải và các dung dịch hóa chất mà không bị ảnh hưởng bởi tính chất ăn mòn của chúng, đảm bảo tuổi thọ và hiệu quả của hệ thống.
Good Heat Resistance
HDPE has a relatively high melting point compared to many other plastics, which gives HDPE products excellent heat resistance. This means that HDPE can be used in high-temperature environments without deforming or losing its functional properties.
This heat resistance is a key advantage in industrial applications, particularly in the food and chemical industries. For instance, HDPE is used to manufacture bottles and containers for products that require storage at elevated temperatures, as well as pipes for transporting hot liquids.
In addition, HDPE can withstand sudden temperature changes without becoming brittle or cracking under harsh conditions. This makes it an ideal material for outdoor products that are exposed to direct sunlight and varying weather elements.
Corrosion Resistance of HDPE
Corrosion resistance is one of the main reasons HDPE is widely used across industries. This property protects products made from HDPE from damage caused by corrosive agents, thereby increasing the lifespan and operational efficiency of HDPE-based equipment.
Applications in Water Supply and Drainage Systems
HDPE has become a top choice for manufacturing water supply pipes, drainage pipes, and related fittings. Its corrosion resistance ensures that the pipes are not affected by corrosive substances present in water, soil, or waste. This helps maintain the quality of clean water and extends the lifespan of water infrastructure systems.
Furthermore, HDPE’s resistance to chemicals found in soil makes it highly effective and safe for use in wastewater treatment systems. It is also used to manufacture storage tanks and chemical containers, providing safe and efficient solutions for storing and transporting corrosive liquids.
Corrosion Resistance in Marine Environments
HDPE is highly resistant to the corrosive effects of seawater and marine organisms, making it an excellent material for protecting underwater and coastal structures.
It is widely used in the production of floating structures, docks, breakwaters, and other marine construction projects. Thanks to its corrosion resistance, these HDPE-based structures have a longer service life and require less maintenance and repair, resulting in cost savings over time.
Moreover, HDPE plays an important role in protecting the marine environment by helping to prevent pollution and maintain ecological balance. Its applications in marine settings are increasingly being explored and developed, contributing to the preservation of valuable ocean resources.
Corrosion Resistance in the Chemical Industry
In the chemical industry, HDPE is used to manufacture equipment for storing, transporting, and handling chemicals. Its excellent corrosion resistance ensures that such equipment remains unaffected by highly corrosive substances, thereby enhancing safety for both operators and the environment.
For example, HDPE is used to make storage tanks, containers, chemical drums, pipelines, and HDPE liners, providing safe and efficient solutions for chemical handling and storage.
The corrosion resistance of HDPE helps prevent chemical leaks, protects human health, and minimizes environmental impact. It also reduces maintenance and replacement costs due to corrosion-related damage, improving overall production efficiency and saving operational costs.
Strength-to-Density Ratio
One of the key advantages that makes HDPE appealing is its high strength-to-density ratio. This means HDPE offers high strength while maintaining a lightweight profile, helping to reduce load and transportation costs.
Molecular Structure & Strength
HDPE features a linear molecular structure with few branches, allowing its molecules to pack tightly together and bond through strong intermolecular forces. This is the primary reason for HDPE’s impressive mechanical strength.
HDPE can withstand tensile, compressive, and impact stress very well. As a result, it is widely used in applications requiring high durability, such as water pipes, containers, and household products.
HDPE has excellent load-bearing capacity—it can handle substantial weight without deforming or breaking.
Density & Lightweight
The density of HDPE ranges from 930 to 970 kg/m³. Compared to other plastics, HDPE has relatively low density, resulting in a lightweight material. This contributes to lower transportation and handling costs.
For example, when used in water pipe production, HDPE’s light weight helps reduce the overall load on the piping system, making installation and transportation easier.
Additionally, HDPE’s lightweight nature helps reduce energy consumption during manufacturing and shipping, contributing to environmental protection and energy savings.
Recyclability
One of the key advantages of HDPE is its recyclability. This helps reduce plastic waste and contributes to environmental protection.
Identification Code & Recycling Process
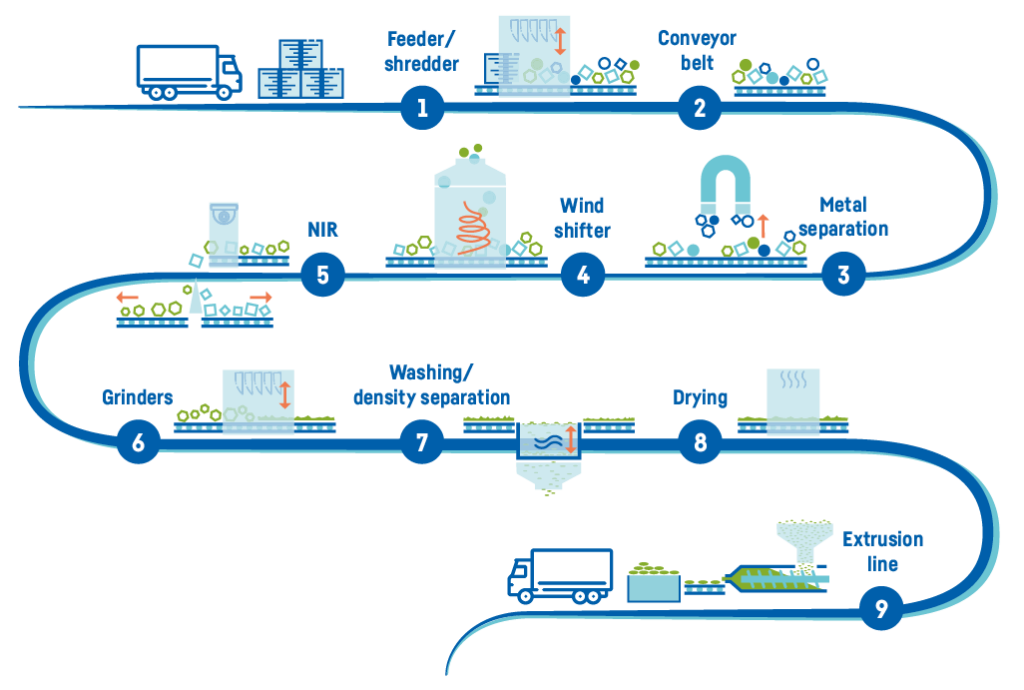
In the plastic waste classification system, HDPE is identified by the code number 2. This code helps individuals easily sort plastic waste and place it in the correct recycling bin, making the recycling process more efficient.
The recycling process of HDPE is quite simple. HDPE is collected, sorted, and cleaned before being fed into a shredder to create recycled plastic pellets. These pellets can then be used to produce new products, such as furniture, construction materials, household items, and more.
Minimizing Environmental Impact
Recycling HDPE helps reduce the amount of plastic waste that ends up in the environment, thereby minimizing soil, water, and air pollution.
Using recycled HDPE also contributes to energy and natural resource conservation, helping to reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
HDPE can be recycled multiple times, which optimizes resource use and reduces reliance on fossil-based raw materials.
Applications of HDPE
Thanks to its superior properties, HDPE is used in a wide range of fields, from everyday consumer products to complex industrial applications.
Food Packaging Applications
HDPE is a plastic material that is safe for human health, free from harmful substances, and does not affect the quality of food.
As a result, HDPE is widely used in the production of food packaging such as water bottles, milk bottles, cosmetic jars, food containers, and more.
Due to its excellent heat resistance, HDPE products can be used to store both hot and cold food without compromising the quality and safety of the food.
 |  |  |
Applications in the Construction Industry
HDPE is used to produce construction materials such as water pipes, drainage pipes, roofing sheets, and floor mats. Its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and heat resistance make these products highly durable, long-lasting, and safe to use.
In the construction industry, HDPE is also used to produce lightweight and sturdy building structures, helping to reduce costs and construction time.
HDPE is an environmentally friendly construction material that can be recycled and reduces waste, contributing to environmental protection.
Applications of HDPE in Healthcare
HDPE is used to manufacture medical equipment such as medicine bottles, syringes, and medical devices.
Its waterproof, corrosion-resistant, and heat-resistant properties help protect medical tools, ensuring hygiene and safety during use.
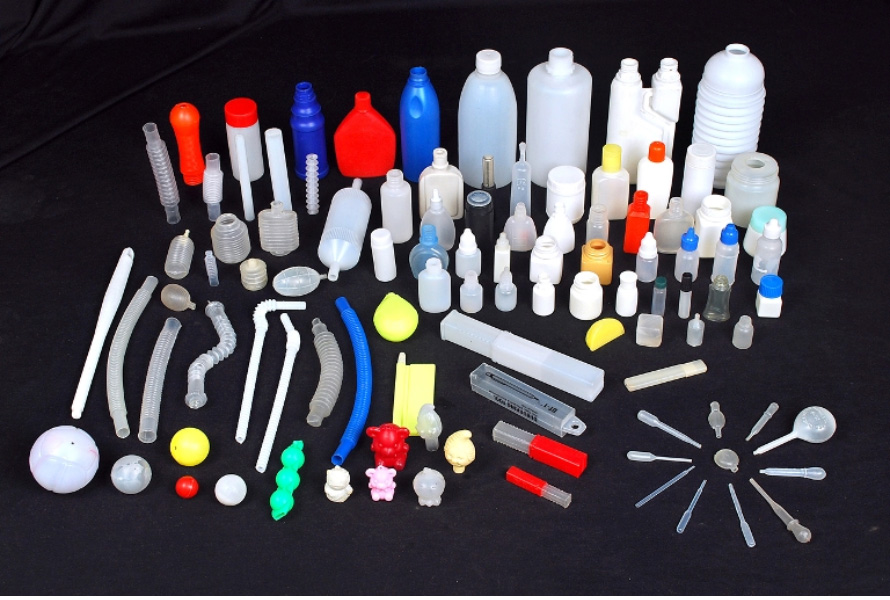

Applications in the Industrial Sector
HDPE is widely used in the production of industrial products such as chemical containers, oil and gas pipelines, automotive parts, household items, and more.
In the chemical industry, HDPE is used to produce tanks, reservoirs, containers, and chemical pipelines, helping to transport and store chemicals safely and efficiently.
HDPE’s excellent heat resistance, corrosion resistance, and high strength ensure these products have a long lifespan and are safe and effective in use.
Conclusion
In conclusion, HDPE is a versatile thermoplastic material with many outstanding properties such as high strength, corrosion resistance, heat resistance, ease of processing, and recyclability. These characteristics have made HDPE popular across various fields, from food packaging production, household goods, to complex industrial applications like water pipelines, chemical containers, and construction materials.
HDPE plays an important role in environmental protection, energy conservation, and natural resource savings. Encouraging the use of recycled HDPE, raising public awareness about waste sorting and plastic recycling, are key factors in protecting the environment and promoting sustainable development.












